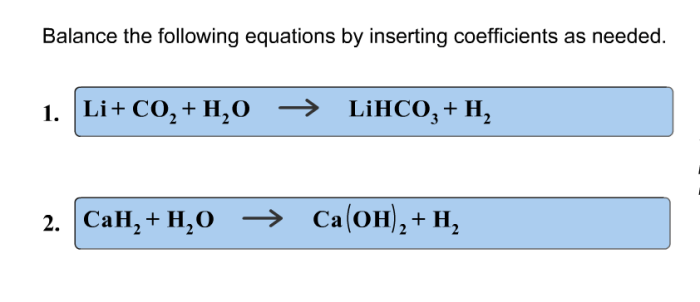
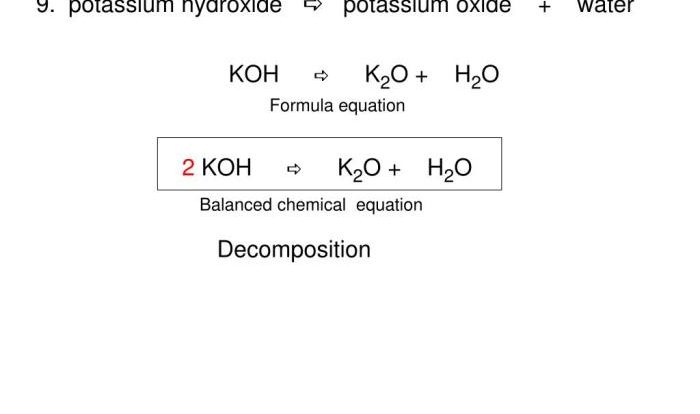
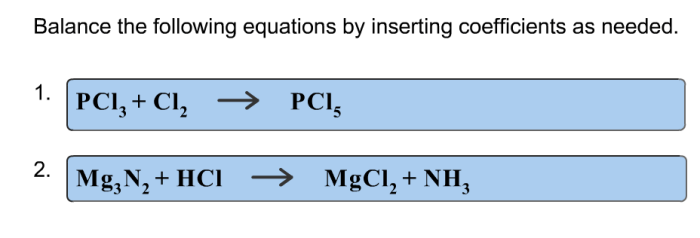
Balance the following equations by inserting coefficients as needed – Balancing chemical equations by inserting coefficients is a fundamental skill in chemistry. It involves adjusting the stoichiometric coefficients of reactants and products to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is identical on both sides of the equation.
This process is crucial for understanding and predicting the outcomes of chemical reactions.
By balancing equations, chemists can determine the mole ratios of reactants and products, calculate reaction yields, and make accurate predictions about the behavior of chemical systems. This knowledge is essential for various applications in chemistry, including chemical synthesis, environmental science, and industrial processes.
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations involves adjusting the coefficients of reactants and products to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. This is necessary because chemical reactions must obey the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed during a reaction.
To balance an equation, follow these steps:
- Write the unbalanced equation.
- Count the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation.
- Adjust the coefficients of the reactants and products to balance the number of atoms of each element.
- Check that the equation is balanced by verifying that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides.
Methods for Balancing Equations, Balance the following equations by inserting coefficients as needed
There are two main methods for balancing chemical equations:
- Oxidation-reduction method:This method involves identifying the oxidation and reduction half-reactions and balancing them separately before combining them to form the overall balanced equation.
- Half-reaction method:This method involves writing the equation as two half-reactions, one for oxidation and one for reduction, and then balancing each half-reaction before combining them to form the overall balanced equation.
The choice of method depends on the complexity of the equation and the experience of the person balancing it.
Stoichiometry and Coefficients
Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. The coefficients in a balanced chemical equation represent the number of moles of each reactant and product involved in the reaction.
For example, the equation:
H2+ O 2→ 2H 2O
indicates that 2 moles of hydrogen gas react with 1 mole of oxygen gas to produce 2 moles of water.
Applications of Balancing Equations
Balancing chemical equations is essential for understanding and predicting the outcome of chemical reactions. It allows chemists to:
- Predict the products of a reaction.
- Calculate the amount of reactants and products involved in a reaction.
- Determine the limiting reactant in a reaction.
- Use stoichiometry to solve problems involving chemical reactions.
General Inquiries: Balance The Following Equations By Inserting Coefficients As Needed
What is the purpose of balancing chemical equations?
Balancing chemical equations ensures that the number of atoms of each element is identical on both sides of the equation, reflecting the law of conservation of mass.
How do I determine the coefficients in a balanced equation?
Coefficients are adjusted until the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides of the equation. This can be achieved through trial and error or by using algebraic methods.
What are the applications of balancing chemical equations?
Balancing chemical equations is essential for calculating reaction yields, predicting product formation, and understanding the stoichiometry of chemical reactions.