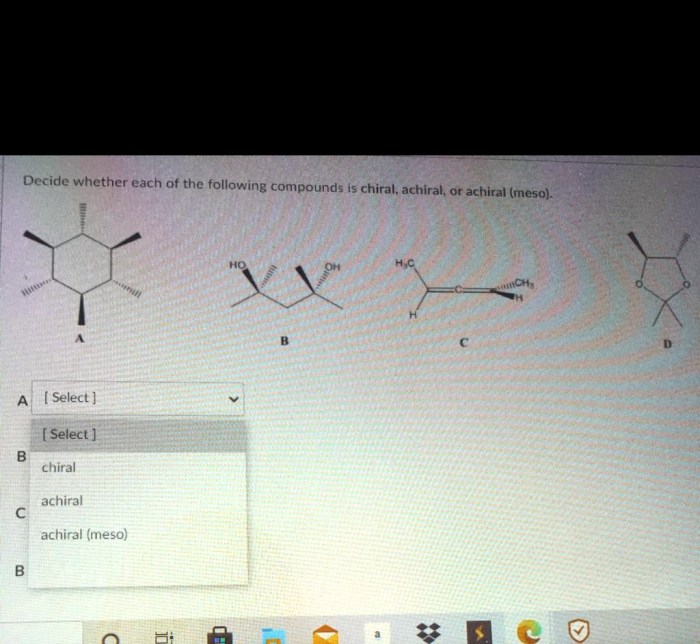
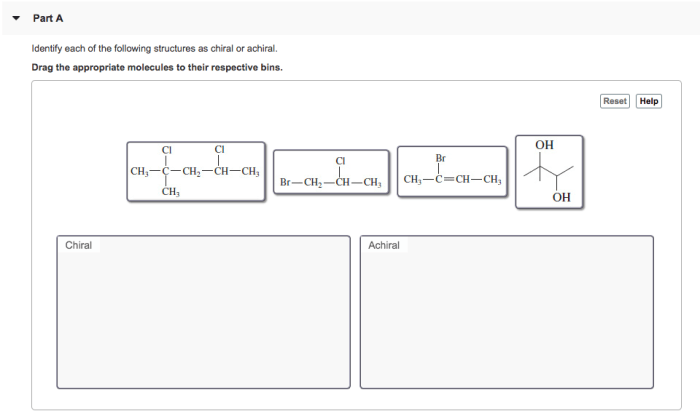
Identify each of the following structures as chiral or achiral – Identifying chiral and achiral structures is a fundamental concept in chemistry that has profound implications in various scientific disciplines. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricate world of chirality and achirality, providing a clear understanding of their significance and the methods employed to distinguish between them.
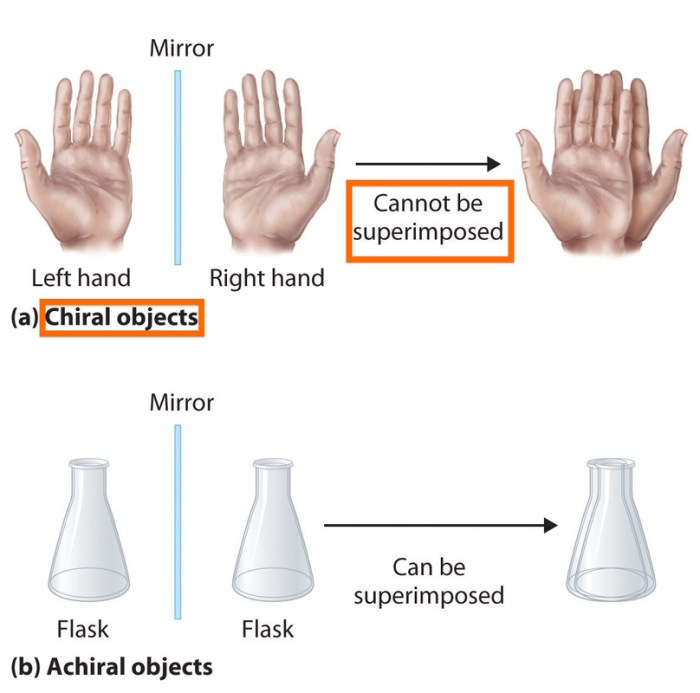
Chirality, derived from the Greek word “cheir” meaning “hand,” refers to the property of an object that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image. In the context of molecules, chirality arises from the presence of a chiral center, which is an atom bonded to four different groups.
Achirality, on the other hand, describes molecules that are superimposable on their mirror images.
Chirality and Achirality in Molecules
In chemistry, chirality refers to the property of a molecule that makes it non-superimposable on its mirror image. In other words, chiral molecules have a handedness, like a right hand and a left hand. Achiral molecules, on the other hand, are superimposable on their mirror images and do not have a handedness.
Chiral Structures
Chiral molecules are characterized by the presence of at least one chiral center, which is a carbon atom that is bonded to four different groups. The arrangement of these groups around the chiral center creates two non-superimposable mirror images, known as enantiomers.
The handedness of a chiral molecule is determined by the relative orientation of the groups around the chiral center.
Achiral Structures
Achiral molecules do not have a chiral center and are superimposable on their mirror images. They can be classified into two types: symmetrical and asymmetrical. Symmetrical molecules have a plane of symmetry that divides the molecule into two identical halves.
Asymmetrical molecules do not have a plane of symmetry, but they may have other types of symmetry, such as rotational symmetry or point symmetry.
Identifying Chirality and Achirality, Identify each of the following structures as chiral or achiral
To determine whether a molecule is chiral or achiral, the following steps can be taken:
- Identify all the chiral centers in the molecule.
- Determine if the molecule has a plane of symmetry.
- If the molecule has a chiral center and no plane of symmetry, then it is chiral.
- If the molecule has no chiral centers or a plane of symmetry, then it is achiral.
User Queries: Identify Each Of The Following Structures As Chiral Or Achiral
What is the difference between a chiral and an achiral molecule?
Chiral molecules are not superimposable on their mirror images, while achiral molecules are superimposable on their mirror images.
How can I determine if a molecule is chiral or achiral?
To determine chirality, identify the presence of a chiral center, which is an atom bonded to four different groups.
What are the implications of chirality in biological systems?
Chirality plays a crucial role in biological systems, as many biomolecules, such as proteins and DNA, exist as chiral molecules.