The Respiratory System Fill in the Blanks delves into the intricate mechanisms of the respiratory system, providing a comprehensive understanding of its anatomy and physiology. This guide offers a thorough exploration of the respiratory system’s components, processes, and functions, equipping readers with a profound knowledge of this vital system.
Through detailed explanations and engaging illustrations, this guide unravels the complexities of the respiratory system, shedding light on its essential role in maintaining life. From the intricate structure of the lungs to the delicate balance of gas exchange, The Respiratory System Fill in the Blanks provides a comprehensive overview of this remarkable system.
The Anatomy of the Respiratory System
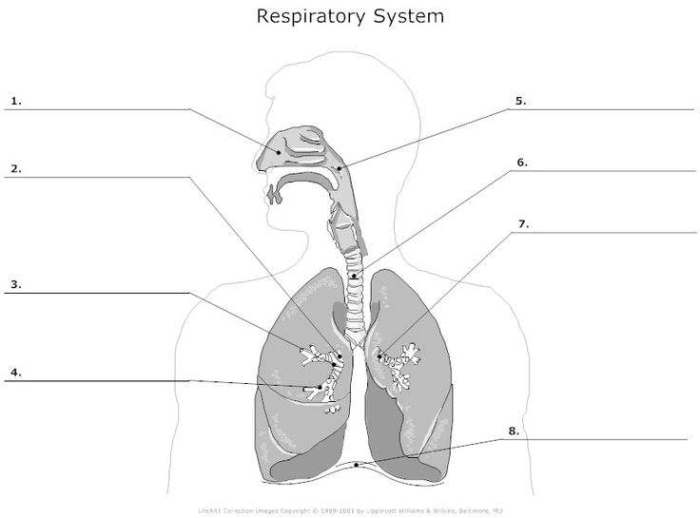
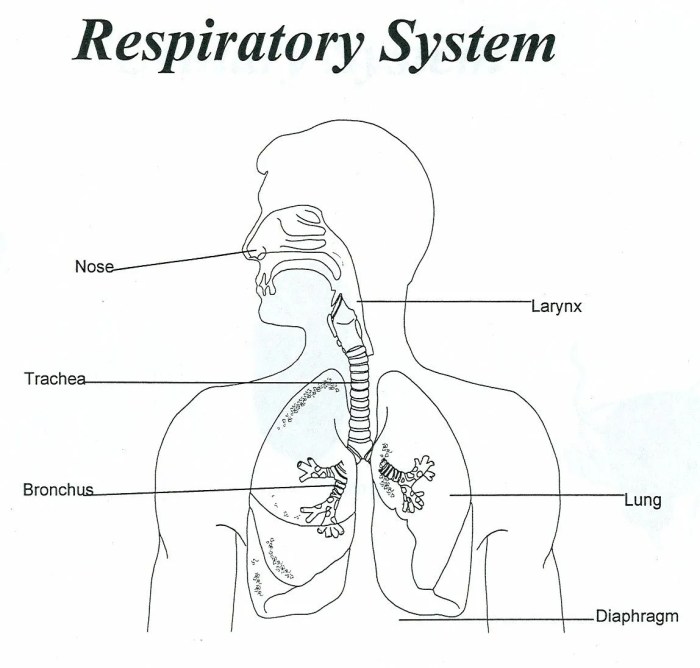
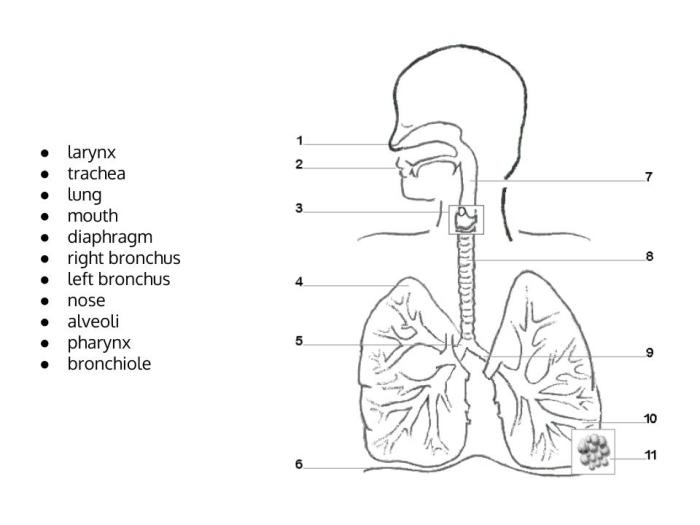
The respiratory system is a complex network of organs and tissues that work together to facilitate the exchange of gases between the body and the external environment. It consists of the following components:
- Nose:The primary entry point for air, the nose is lined with mucus-producing cells that trap dust and other particles.
- Pharynx:A muscular tube that connects the nose and mouth to the larynx.
- Larynx:Commonly known as the voice box, the larynx contains the vocal cords that produce sound.
- Trachea:A flexible tube that carries air from the larynx to the lungs.
- Bronchi:The two primary branches of the trachea that enter the lungs.
- Lungs:Two spongy organs located in the chest cavity that are responsible for gas exchange.
The Physiology of the Respiratory System
Respiration, the process of gas exchange, involves two primary phases: inhalation and exhalation.
Inhalation:During inhalation, the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, expanding the chest cavity. This creates a negative pressure that draws air into the lungs.
Exhalation:During exhalation, the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, reducing the volume of the chest cavity. This forces air out of the lungs.
Gas exchange occurs in the lungs, where oxygen from the air diffuses into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide from the bloodstream diffuses into the air.
The Respiratory System and Gas Exchange: The Respiratory System Fill In The Blanks
Partial pressure, the pressure exerted by a specific gas in a mixture, plays a crucial role in gas exchange.
Oxygen and carbon dioxide move down their respective partial pressure gradients. Oxygen, with a higher partial pressure in the lungs than in the bloodstream, diffuses into the bloodstream.
Hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, binds to oxygen and transports it throughout the body.
Factors such as altitude and exercise can affect gas exchange by altering partial pressures.
The Respiratory System and pH Balance
The respiratory system plays a critical role in maintaining the body’s pH balance.
Respiratory acidosisoccurs when there is an increase in carbon dioxide levels, leading to a decrease in pH.
Respiratory alkalosisoccurs when there is a decrease in carbon dioxide levels, leading to an increase in pH.
These conditions can have significant clinical implications, affecting organ function and overall health.
The Respiratory System and Thermoregulation
The respiratory system contributes to thermoregulation, the process of maintaining body temperature.
Panting, a rapid and shallow breathing pattern, helps cool the body by increasing evaporative heat loss.
Extreme temperatures can affect the respiratory system, causing conditions such as hypothermia and heat stroke.
The Respiratory System and Defense Mechanisms
The respiratory system is involved in defending against pathogens.
The respiratory tract is lined with immune cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, that recognize and destroy pathogens.
The respiratory system also produces mucus, which traps and removes pathogens.
General Inquiries
What are the main functions of the respiratory system?
The respiratory system is responsible for gas exchange, oxygen uptake, and carbon dioxide removal. It also plays a role in pH balance, thermoregulation, and defense against pathogens.
How does the respiratory system contribute to pH balance?
The respiratory system helps regulate pH balance by adjusting the levels of carbon dioxide in the blood. Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form carbonic acid, which can lower blood pH. By exhaling carbon dioxide, the respiratory system helps maintain a healthy pH level.
What are some common respiratory diseases?
Common respiratory diseases include asthma, bronchitis, pneumonia, and lung cancer. These diseases can affect the structure and function of the respiratory system, leading to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest pain.