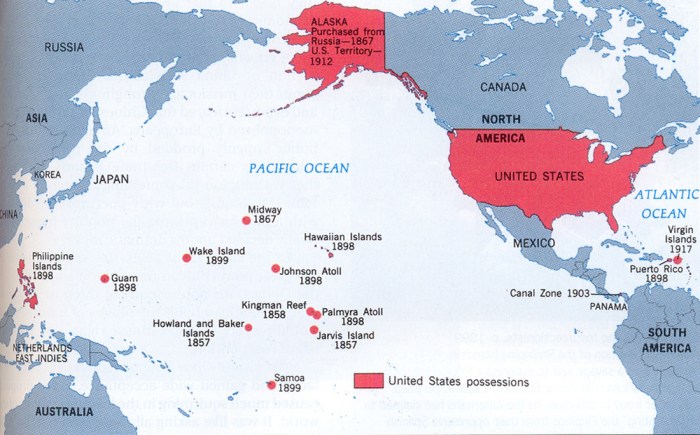
The u.s. takes hawaii leader or bully – The US: Leader or Bully in Hawaii? sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This captivating exploration delves into the historical, cultural, and economic implications of the US involvement in Hawaii, providing a comprehensive analysis of a complex and multifaceted relationship.
The second paragraph delves deeper into the topic, providing a descriptive and clear overview of the historical events leading to the US annexation of Hawaii. It discusses the role of US economic and political interests in the annexation, presenting a balanced perspective that considers both Hawaiian and American viewpoints.
Historical Context: The U.s. Takes Hawaii Leader Or Bully

The annexation of Hawaii by the United States was a complex and controversial event that occurred in 1898. The historical context leading to this annexation can be traced back to the arrival of American missionaries and traders in Hawaii in the early 19th century.
These individuals played a significant role in introducing Western culture and values to the Hawaiian islands, which gradually weakened the traditional Hawaiian monarchy and social structure.
As the United States expanded its influence in the Pacific region, it became increasingly interested in acquiring Hawaii as a strategic military outpost. The presence of Pearl Harbor, a natural deep-water harbor, made Hawaii particularly valuable for the US Navy.
Additionally, the United States had significant economic interests in Hawaii, particularly in the sugar industry, which was the islands’ main source of revenue.
Perspectives on US Involvement
The annexation of Hawaii has been the subject of much debate and controversy, with different perspectives on the role of the United States in the event. From the Hawaiian perspective, many saw the annexation as an act of imperialism and a violation of their sovereignty.
The Hawaiian monarchy was overthrown in 1893 by a group of American businessmen and planters, and the islands were formally annexed by the United States in 1898. This led to the loss of Hawaiian independence and the imposition of American laws and customs.
From the American perspective, the annexation was seen as a necessary step to protect American interests in the Pacific region. The United States argued that Hawaii was strategically important for its military and that the annexation was necessary to maintain stability in the region.
Additionally, the United States claimed that the annexation was in the best interests of the Hawaiian people, as it would bring them the benefits of American civilization and economic prosperity.
Impact on Hawaiian Culture and Society
The annexation of Hawaii had a profound impact on Hawaiian culture and society. The traditional Hawaiian monarchy was abolished, and the islands were subjected to American laws and customs. This led to a decline in the Hawaiian language and culture, as well as the loss of traditional Hawaiian lands and resources.
Additionally, the annexation brought about significant social and economic changes, as the Hawaiian economy became increasingly dependent on the United States.
One of the most significant impacts of the annexation was the loss of Hawaiian sovereignty. The Hawaiian monarchy had been a symbol of Hawaiian independence and culture, and its overthrow and the subsequent annexation of the islands by the United States was a major blow to Hawaiian pride and identity.
The loss of sovereignty also led to the loss of Hawaiian lands and resources, as the United States government took control of vast tracts of land for military bases and other purposes.
US Influence on Hawaii’s Economy and Development, The u.s. takes hawaii leader or bully
The annexation of Hawaii had a significant impact on the islands’ economy and development. The United States brought about a number of changes to the Hawaiian economy, including the introduction of a new currency, the establishment of a banking system, and the development of new industries, such as tourism and agriculture.
The United States also invested heavily in infrastructure, including the construction of roads, railroads, and harbors.
The annexation of Hawaii also led to the development of a new social and economic elite in Hawaii. This elite was composed of American businessmen and planters, who controlled the islands’ economy and politics. The annexation also led to the immigration of a large number of non-Hawaiian workers, who were brought to the islands to work on the sugar plantations and other industries.
Contemporary Issues and Debates
The annexation of Hawaii continues to be a topic of debate and controversy in contemporary times. Some Native Hawaiians argue that the annexation was illegal and that the United States government has an obligation to restore Hawaiian sovereignty. There are also ongoing debates about the impact of the annexation on Hawaiian culture and society, as well as the role of the United States military in Hawaii.
One of the most pressing contemporary issues related to the annexation of Hawaii is the issue of Hawaiian sovereignty. Native Hawaiians have long argued that the annexation was illegal and that the United States government has an obligation to restore Hawaiian sovereignty.
This issue has been the subject of numerous legal challenges and political debates, and it remains a major point of contention between Native Hawaiians and the United States government.
Questions Often Asked
What were the main reasons for US involvement in Hawaii?
The US involvement in Hawaii was primarily driven by economic and strategic interests, including the desire for a naval base in the Pacific and the expansion of American agricultural and commercial activities.
How did US annexation affect Hawaiian culture and society?
US annexation had a significant impact on Hawaiian culture and society, leading to the suppression of the Hawaiian language and traditions, as well as the introduction of American values and institutions.
What are the current debates surrounding US presence in Hawaii?
Current debates surrounding US presence in Hawaii focus on issues such as Hawaiian sovereignty, self-determination, and the ongoing legacy of colonialism.